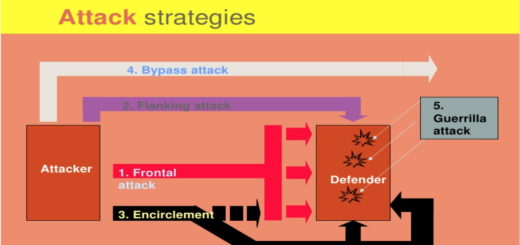
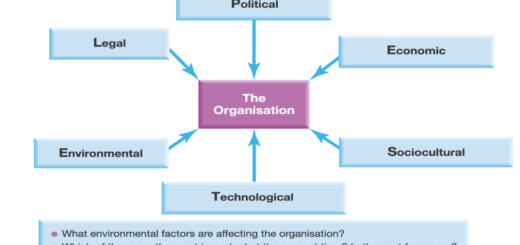
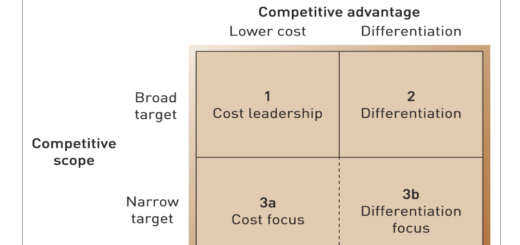
Motivation
Concept of Motivation:
Motivation refers to the psychological processes that activate, direct, and sustain goal-directed behavior. In other words, it’s the internal or external factors that drive individuals to engage in certain behaviors, sustain their efforts over time, and reach their desired outcomes.
One famous scholar who has contributed significantly to the understanding of motivation is Abraham Maslow. He proposed the hierarchy of needs theory, which suggests that human needs can be arranged in a hierarchical order. Maslow believed that individuals are motivated by fulfilling their basic physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs, in that order.
Maslow argued that individuals will not be motivated to pursue higher-level needs until their basic needs are met. For example, individuals will not be motivated to pursue self-actualization, such as a creative expression or personal growth, until their lower-level needs for food, shelter, and safety are satisfied.
According to the Self-Determination Theory by Edward L. Deci and Richard M. Ryan, motivation is categorized into three types:
- Intrinsic motivation: It is the type of motivation where an individual is motivated by internal factors like personal interest, enjoyment, or the satisfaction of performing a task.
- Extrinsic motivation: It is the type of motivation where an individual is motivated by external factors like rewards, recognition, or punishments.
- Amotivation: It is the absence of motivation where an individual lacks the drive or desire to perform a task.
Motivation can be influenced by various factors such as personal values, beliefs, emotions, social norms, and cultural factors. It is an essential component in achieving success, satisfaction, and personal growth.
Overall, motivation is a complex concept that can be influenced by various factors, including individual characteristics, social context, and environmental factors.