Henry Mintzberg: Ten Roles of Manager
Henry Mintzberg is a renowned management scholar and author who has made significant contributions to the field of management theory. One of his key contributions is his classification of ten management roles that managers perform in order to fulfill their responsibilities. These ten roles are grouped into three categories: interpersonal, informational, and decisional.
The interpersonal roles include:
The interpersonal roles of management involve building relationships, leading and communicating with others, and representing the organization to stakeholders. These roles are important for establishing trust, motivation, and a sense of shared purpose among employees, and for ensuring that the organization is able to effectively achieve its goals.
- Figurehead: This role involves acting as the symbolic head of the organization and performing ceremonial and symbolic duties. The manager acts as a figurehead for the organization and represents it to the public, stakeholders, and employees.
- Leader: This role involves motivating and directing subordinates, and providing guidance and support to achieve organizational goals. The manager acts as a leader to help employees achieve their full potential and to achieve the objectives of the organization.
- Liaison: This role involves maintaining relationships with other organizations and individuals, both within and outside the organization. The manager acts as a liaison to foster good relationships, exchange information, and resolve conflicts.
The informational roles include:
Informational roles in management involve the gathering and dissemination of information within an organization. These roles are essential for ensuring that managers have the information they need to make informed decisions and keep employees informed about the organization’s goals, plans, and activities.
There are three main informational roles in management, as described by Henry Mintzberg:
- Monitor: This role involves gathering information from internal and external sources, and keeping abreast of changes and developments in the organization and its environment. The manager acts as a monitor to identify opportunities and threats and to ensure that the organization is responsive to changes in its environment.
- Disseminator: This role involves communicating information to others within the organization, and sharing knowledge and ideas to improve organizational performance. The manager acts as a disseminator to ensure that employees have the information they need to do their jobs effectively, and to promote collaboration and cooperation among team members.
- Spokesperson: This role involves communicating information to external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, and the general public. The manager acts as a spokesperson to maintain good relationships with external stakeholders and to ensure that the organization is well-regarded by its stakeholders.
Informational roles are important for ensuring that managers have access to relevant information, and for promoting effective communication and collaboration within and outside the organization.
The Decisional Roles:
Decisional roles in management involve making decisions, solving problems, and taking action to achieve the objectives of the organization. These roles require managers to use their judgment, problem-solving skills, and decision-making abilities to make informed and effective decisions.
- Entrepreneur: This role involves initiating change and taking risks to improve organizational performance and achieve new opportunities. The manager acts as an entrepreneur to create new initiatives, implement new strategies, and drive innovation within the organization.
- Disturbance Handler: This role involves resolving conflicts and solving problems that arise within the organization. The manager acts as a disturbance handler to ensure that issues are addressed in a timely and effective manner, and to maintain a positive work environment.
- Resource Allocator: This role involves making decisions about the allocation of resources, such as time, money, and personnel, to achieve the objectives of the organization. The manager acts as a resource allocator to ensure that the organization’s resources are used effectively and efficiently.
- Negotiator: This role involves representing the organization in negotiations with other organizations and individuals. The manager acts as a negotiator to reach an agreement on key issues, such as contracts, partnerships, and collaborations.
Mintzberg’s ten management roles provide a useful framework for understanding the diverse tasks that managers perform on a daily basis and help to highlight the complex and multi-faceted nature of management.

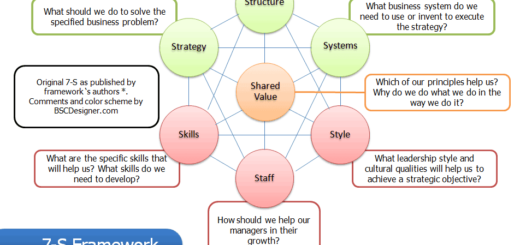
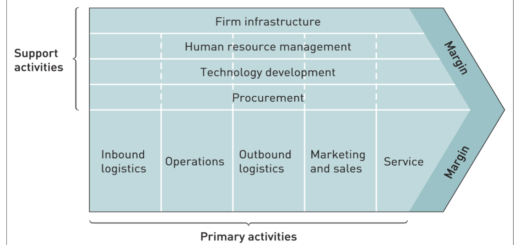


Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. A fantastic read. I will definitely be back.