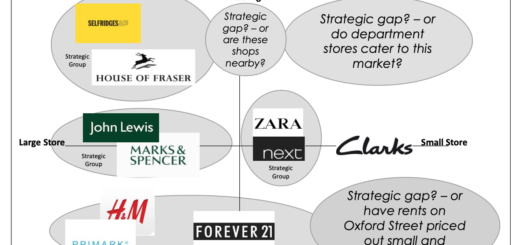
Competitors Strategies
Attack Strategies:
An attack strategy in business refers to a plan or a set of tactics that a company uses to gain a competitive advantage over its rivals. This can involve aggressive marketing tactics, undercutting prices, or developing new and innovative products that are more appealing to customers. Attack strategies can be effective in driving growth and profitability, but they also carry risks such as damaging brand reputation, creating negative perceptions among consumers, and even legal consequences if tactics violate industry regulations or laws. Successful attack strategies require a thorough understanding of the market, competitors, and customer needs, as well as careful planning and execution.
Defense Strategies:
Defense strategies of business refer to tactics and actions that companies take to protect their market position, reputation, and profitability against threats from competitors, new entrants, or changing market conditions.
Types of Attacks Strategies:
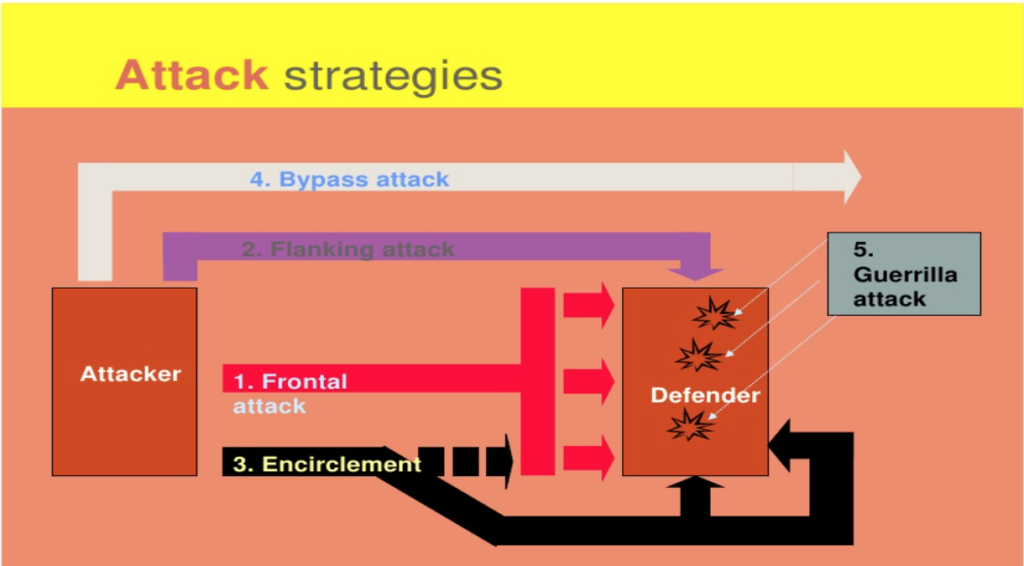
Kotler’s Attack Strategy:
Market Challengers Strategies – A way to attack to increase market share.
Frontal Attack:
A frontal attack strategy in business is a tactic where a company directly competes with its competitors in the same market by offering similar products or services. This involves going head-to-head with competitors in terms of price, quality, features, and marketing. In a frontal attack strategy, the goal is to gain market share and increase revenue by capturing customers from competitors. For example, a company may launch a new product that is similar to a competitor’s but offers better features or is priced lower. The company may also invest heavily in marketing to promote the product and differentiate it from competitors. The aim is to attract customers who are currently buying from competitors and convince them to switch to the company’s product.
- Direct challenge (differential advantage)
- Direct attack (distinctive competence)
- Direct attack (market share)
Flank attack:
Flank attack strategies are tactics that involve targeting a competitor’s weaknesses or areas of vulnerability. This type of attack strategy is called a “flank” attack because it involves attacking the competitor on their weaker side, rather than directly targeting their strengths. Some examples of flank attack strategies include:
- Niche targeting: This involves targeting a specific customer segment or market niche that the competitor is not serving. By identifying an untapped market, the attacking business can gain market share without directly competing with the competitor.
- Product differentiation: This involves creating a product or service that is unique and different from the competitor’s offering. By creating a distinctive product or service, the attacking business can capture market share and differentiate itself from the competitor.
- Marketing differentiation: This involves creating a marketing campaign that highlights the differences between the attacking business and the competitor. For example, the attacking business might emphasize its superior customer service or faster delivery times.
- Distribution channels: This involves targeting a different distribution channel than the competitor. By reaching customers through a different channel, such as online sales or a different retail chain, the attacking business can gain market share without directly competing with the competitor.
Flank attack strategies are a lower-risk alternative to frontal attack strategies, as they involve targeting a competitor’s weakness rather than their strengths. However, they also require careful planning and execution to identify the right target and capitalize on the opportunity.
Encirclement:
The encirclement attack strategy is a tactic that involves attacking a competitor on multiple fronts, in an attempt to surround and overwhelm them. This type of attack is called an “encirclement” attack because it involves attacking the competitor from all sides, similar to a military siege.
Some examples of encirclement attack strategies include:
- Product-line expansion: This involves creating a wide range of products that compete with the competitor’s products across multiple product lines. By offering a wider range of products, the attacking business can capture market share across the entire product range.
- Distribution channel expansion: This involves creating multiple distribution channels that reach customers in different geographic locations. By expanding the distribution network, the attacking business can capture market share in different regions.
- Price undercutting: This involves offering products or services at lower prices than the competitor across multiple product lines. By offering lower prices, the attacking business can capture market share from price-sensitive customers.
- Marketing campaigns: This involves creating a marketing campaign that targets the competitor across multiple channels, such as online ads, billboards, and television ads. By saturating the market with marketing campaigns, the attacking business can increase brand awareness and capture market share.
The encirclement attack strategy can be effective because it puts the competitor under pressure from all sides. However, it can also be risky because it requires a significant investment of resources, and there is a chance that the competitor will respond with counterattacks. Therefore, careful planning and execution are necessary to successfully implement encirclement attack strategies.
Bypass
A bypass strategy is a tactic that involves avoiding the competitor altogether by finding new markets or creating new products or services that do not compete directly with the competitor. This type of strategy is called a “bypass” because it involves going around the competitor rather than directly confronting them.
Some examples of bypass strategies include:
- Vertical integration: This involves acquiring or developing the capability to produce goods or services that the competitor is currently purchasing from suppliers. By integrating vertically, the attacking business can bypass the competitor and capture market share by producing their own goods or services.
- Geographic expansion: This involves entering new geographic markets where the competitor does not currently operate. By expanding into new regions, the attacking business can capture market share without directly competing with the competitor.
- Product innovation: This involves creating new products or services that are not currently being offered by the competitor. By offering unique products or services, the attacking business can capture market share without directly competing with the competitor.
- Strategic alliances: This involves forming partnerships with other businesses to gain access to new markets or technologies. By forming strategic alliances, the attacking business can bypass the competitor and gain access to new customers or capabilities.
The bypass strategy can be effective because it allows a business to capture market share without directly confronting the competitor. However, it can also be risky because it requires a significant investment of resources and there is a chance that the competitor will respond with counterattacks. Therefore, careful planning and execution are necessary to successfully implement bypass strategies.
Guerrilla
A guerrilla attack strategy is a tactic that involves using unconventional means to attack a competitor, such as through surprise, speed, and asymmetry. This type of strategy is called a “guerrilla” attack because it involves using tactics that are similar to those used by guerrilla fighters in warfare.
Some examples of guerrilla attack strategies include:
- Stealth marketing: This involves creating buzz for a product or service through unconventional marketing methods such as viral marketing, word-of-mouth, or guerilla advertising. By using unconventional marketing tactics, the attacking business can generate interest and capture market share without directly confronting the competitor.
- Low-cost pricing: This involves offering a product or service at a much lower price than the competitor, with the aim of capturing market share from price-sensitive customers. By offering a lower price, the attacking business can attract customers away from the competitor, even if the competitor has a stronger brand.
- Nimble response: This involves quickly responding to changes in the market, such as new product introductions or changing customer preferences. By being nimble and quick to respond, the attacking business can capture market share from the competitor, who may be slower to adapt to market changes.
- Focus on a specific niche: This involves targeting a specific niche market that the competitor is not currently serving, and creating a product or service that meets the unique needs of that niche. By focusing on a small, underserved market, the attacking business can capture market share without directly competing with the competitor.
The guerrilla attack strategy can be effective because it allows a business to capture market share through unconventional means. However, it can also be risky because it may involve tactics that are considered unethical or illegal, such as ambush marketing or hacking. Therefore, careful planning and execution are necessary to successfully implement guerrilla attack strategies while adhering to ethical and legal guidelines.