Leadership: Trait Theory
Leadership is the ability to inspire and influence others towards a common goal or vision. At its core, leadership involves using one’s personal qualities, skills, and knowledge to guide and motivate others in pursuit of a shared objective. Leaders may come from any level of an organization or society, and can exhibit a wide range of styles and approaches to leadership.
Here are some definitions of leadership by different scholars:
- Warren Bennis: “Leadership is the capacity to translate vision into reality.”
- John C. Maxwell: “Leadership is influence – nothing more, nothing less.”
- Peter Drucker: “The only definition of a leader is someone who has followers.”
- “Leadership is the art or process of influencing people so that they will strive willingly and enthusiastically towards the achievement of the organization’s purpose”
- “Leadership is a process whereby an individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal”
- Multiple definitions but commonly a form of behaving that is associated with the process of influence

Trait Theory of Management
Trait theory of management is a leadership theory that focuses on identifying the specific traits or characteristics that make a person a successful leader. The theory asserts that effective leadership is dependent on certain inherent qualities or traits that are possessed by leaders, rather than on skills and knowledge acquired through education or training.
According to trait theory, some of the key leadership traits that contribute to effective leadership include intelligence, self-confidence, determination, integrity, sociability, and emotional stability. The theory holds that individuals with these traits are more likely to emerge as leaders, as they possess the necessary qualities that allow them to lead and motivate others.
Trait theory was first proposed in the early 20th century, and it remains a popular framework for understanding leadership today. While some critics argue that the theory oversimplifies the complex nature of leadership, others believe that it is a useful tool for identifying potential leaders and developing leadership skills.
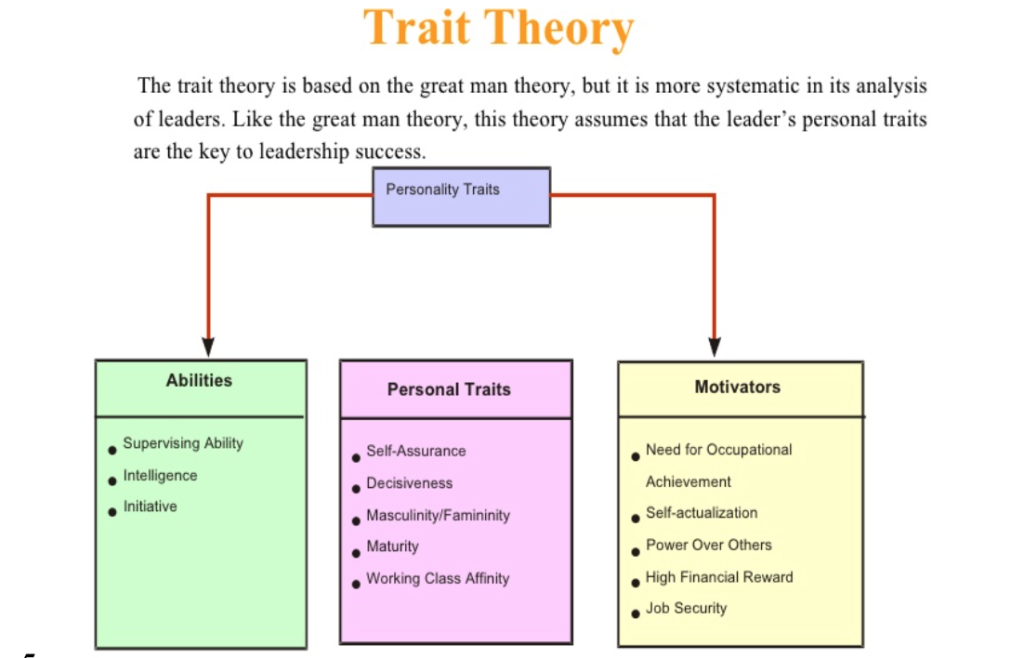
Personality Traits: Abilities, Motivators & personnel Traits
- Abilities: Abilities refer to a person’s natural or acquired talents, skills, and knowledge that enable them to perform certain tasks or activities. Abilities are often associated with cognitive and physical capacities, such as analytical thinking, verbal communication, hand-eye coordination, or problem-solving. Abilities can be developed through training and practice, but they are also influenced by genetics and early life experiences.
- Motivators: Motivators refer to the internal factors that drive a person’s behavior and actions. Motivators can be positive or negative, and they can be categorized into intrinsic or extrinsic motivators. Intrinsic motivators are related to the individual’s interests, passions, or values, while extrinsic motivators are related to external rewards or incentives, such as money, status, or recognition. Understanding an individual’s motivators can help managers and leaders to create a work environment that is more engaging, meaningful, and satisfying.
- Personal Traits: Personal traits refer to the enduring characteristics or tendencies that shape a person’s behavior and attitude. Personal traits can include personality traits, values, attitudes, beliefs, and preferences. Unlike abilities, personal traits are not necessarily related to a specific task or activity, but they can influence a person’s performance and interactions with others. Personal traits can be measured through assessments, such as personality tests, values inventories, or behavioral interviews, and they can be used to inform various HR processes, such as hiring, promotion, or career development.