Ansoff’s Product-Market Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic planning tool developed by Igor Ansoff, a Russian-American mathematician and business theorist. The matrix is designed to help businesses identify new growth opportunities by analyzing four strategic options. The purpose of the Ansoff Matrix is to provide a framework for organizations to develop their market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification strategies.
The main objective of the Ansoff Matrix is to help businesses make informed decisions about how to grow their revenue and increase market share. The matrix provides a clear understanding of the potential risks and rewards associated with each of the four strategic options. This helps businesses to determine the most appropriate approach for their specific circumstances.
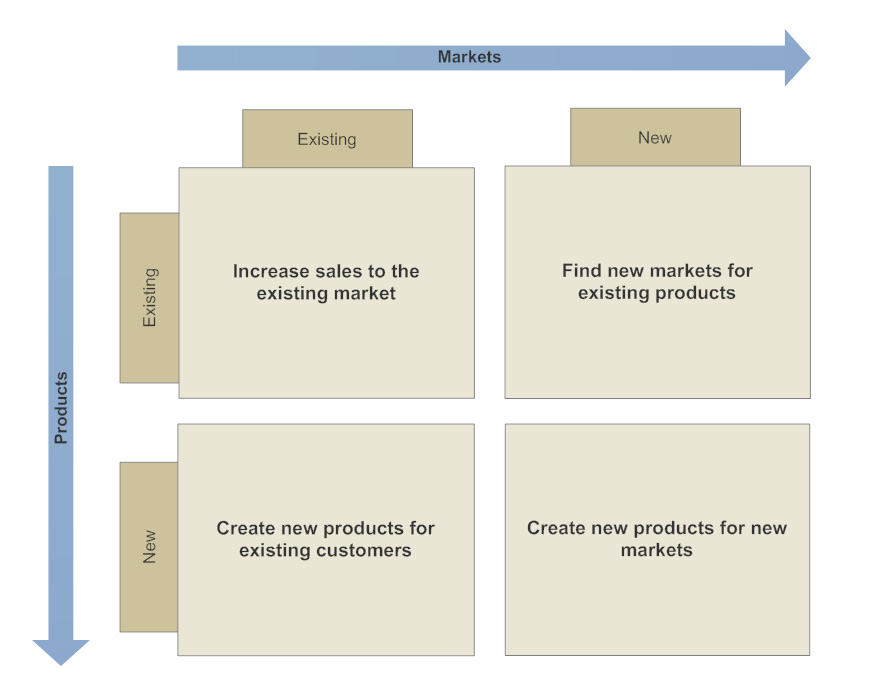
The four strategic options of the Ansoff Matrix are as follows:
Market penetration – a strategy of increasing share of current markets with the current product range. This involves selling more existing products or services to existing customers.
This strategy:
- builds on established strategic capabilities;
- means the organization’s scope is unchanged;
- leads to greater market share and with buyers and suppliers – increased power;
- provides greater experience curves and benefits as well as economies of scale.
Market development – a strategy by which an organization offers existing products to new markets. This involves selling existing products or services to new markets or customer segments.
This strategy involves varying degrees of related diversification (in terms of markets) it;
- can take the form of attracting new users (e.g. extending the use of IT to younger or older users);
- can take the form of new geographies (international markets being the most important);
- may require new strategic capabilities, especially in marketing.
Product development – a strategy by which an organization delivers modified or new products to existing markets. This involves creating new products or services to sell to existing markets or customers.
This strategy:
- involves varying degrees of related diversification (in terms of products);
- can be an expensive and high risk
- may require new strategic capabiliti
Diversification – involves increasing the range of products or markets served by an organization. This involves creating new products or services to sell to new markets or customer segments.
- Related diversification involves diversifying into products or services with relationships to the existing business.
- Conglomerate (unrelated) diversification involves diversifying into products or services with no relationships to existing businesses.
By using the Ansoff Matrix, businesses can evaluate their existing position, assess the market potential, and choose the most appropriate growth strategy to achieve their long-term goals. The Ansoff Matrix is a widely used tool in business strategy and has been applied across various industries and business sectors.
Example:
For example, a company that has been successful in selling high-end smartphones to the US market may use Ansoff’s matrix to explore different growth opportunities.
- Market Penetration: The company may focus on increasing its market share in the existing US market by investing in marketing campaigns, offering discounts, and improving its distribution channels to gain a larger customer base.
- Product Development: The company may decide to develop new features or variations of its existing high-end smartphones to attract new customers within the US market.
- Market Development: The company may expand its sales to other countries, such as Canada or Europe, with its existing high-end smartphones.
- Diversification: The company may diversify its product offerings by introducing a new line of mid-range smartphones, which can cater to a different market segment than its existing high-end smartphones.
By evaluating and selecting the appropriate growth strategy using the Ansoff Matrix, the company can effectively plan and execute its growth plan, thereby achieving its desired business objectives.



I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also
go to see this web site on regular basis to take updated from newest news.
Check out my webpage – fire writing generator
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also
go to see this web site on regular basis to take updated from newest news.
Check out my webpage – fire writing generator
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also
go to see this web site on regular basis to take updated from newest news.
Check out my webpage – fire writing generator
I’m gone to tell my little brother, that he should also
go to see this web site on regular basis to take updated from newest news.
Check out my webpage – fire writing generator