Measures of Effectiveness – Mullins
Laurie J. Mullins, a British management author and academic, has written extensively on management and organizational behavior. In his book “Management and Organisational Behaviour” (2013), Mullins highlights that managers are often evaluated based on the performance of their staff and the overall success of their team. Measuring the effectiveness of management can be challenging, as some aspects, such as motivation, morale, and organizational culture, can be difficult to quantify. However, various indicators can help assess management effectiveness. Some of these measures include:
- Staff turnover: High staff turnover can be an indication of poor management, as it may reflect employee dissatisfaction or lack of development opportunities. A low turnover rate may suggest that employees are content with their work environment and the support they receive from their managers.
- Absenteeism: Frequent employee absences may indicate low morale, dissatisfaction, or poor working conditions. Monitoring absenteeism rates can help identify potential issues that may require managerial attention.
- Sickness: High levels of sickness can be a sign of stress or poor working conditions. Tracking sickness rates can help managers identify areas for improvement in the work environment and employee well-being.
- Timekeeping: Frequent tardiness or poor time management among staff members may reflect a lack of motivation, inadequate supervision, or unclear expectations. Managers can use timekeeping data to identify patterns and address any underlying issues.
- Accidents at work: A high number of workplace accidents may indicate inadequate safety measures, insufficient training, or poor management practices. Monitoring accident rates can help managers identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes.
In some workplaces, additional measures of effectiveness can include:
- Meeting deadlines: The ability of a team to consistently meet deadlines can be an indicator of effective management, as it demonstrates planning, prioritization, and execution capabilities.
- Accuracy or recorded errors: Monitoring the accuracy of work and the number of errors can help assess the quality of management, as it reflects the level of supervision, training, and attention to detail.
- Level of complaints: Frequent complaints from clients, other departments, or suppliers may indicate issues with management practices or team performance. Tracking and addressing these complaints can help improve overall management effectiveness.
- Keeping within budget: Effective financial management is a key aspect of overall management performance. Managers who consistently keep their projects or departments within budget demonstrate strong planning and resource allocation skills.
- Productivity: Monitoring productivity levels can help assess the efficiency and effectiveness of a manager’s team. High productivity may indicate strong motivation, clear goals, and efficient use of resources, while low productivity may point to issues that need to be addressed.
By monitoring these measures, organizations can gain insights into the effectiveness of their managers and identify areas for improvement or development.



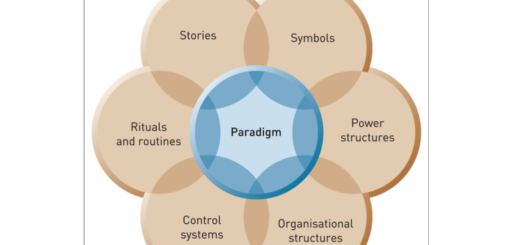
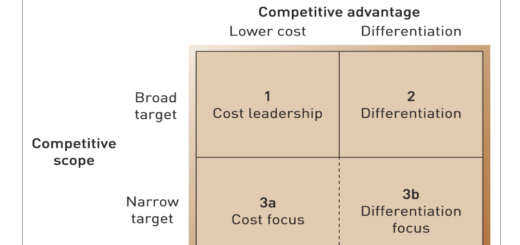
1 Response
[…] What are the measures of effectiveness? […]